What You’ll Learn
- Discover how research-grade, modular labs help engineering departments meet ABET outcomes while producing industry-ready graduates and stronger publishable results.
- Learn a practical approach to building scalable lab systems, starting with core automation units and expanding into PLC, SCADA, and Smart Factory setups.
- Understand how hands-on experimental validation saves students and researchers time by exposing real-world noise, nonlinearity, and faults that simulations miss.
- Identify the fresh idea that modern teaching labs are not demo kits, they are Digital Twin-ready research instruments that mirror industrial conditions.
In the current landscape of higher education, engineering departments face a significant challenge: the divergence between complex theoretical models and the physical reality of experimental validation.
As industrial systems move toward autonomous operation, the pedagogical tools used in undergraduate and graduate programs must transcend basic demonstration kits. For institutions seeking to maintain high-impact research and align with global accreditation standards like ABET, the implementation of scalable, research-grade laboratory systems is a strategic necessity.
The integration of mechatronics automation within a modular laboratory environment allows for the rigorous testing of dynamic system responses, stability assessment, and the implementation of sophisticated control strategies. These platforms are not merely educational aids; they are complex instruments designed to replicate industrial conditions with high fidelity.
Experimental Validation of Theoretical Models
A core pillar of engineering education is the transition from mathematical abstraction to physical verification. In disciplines such as Control Engineering and Process Control, students must move beyond software simulation to witness the non-linearities and stochastic disturbances inherent in physical hardware.
PID Tuning and Controller Design
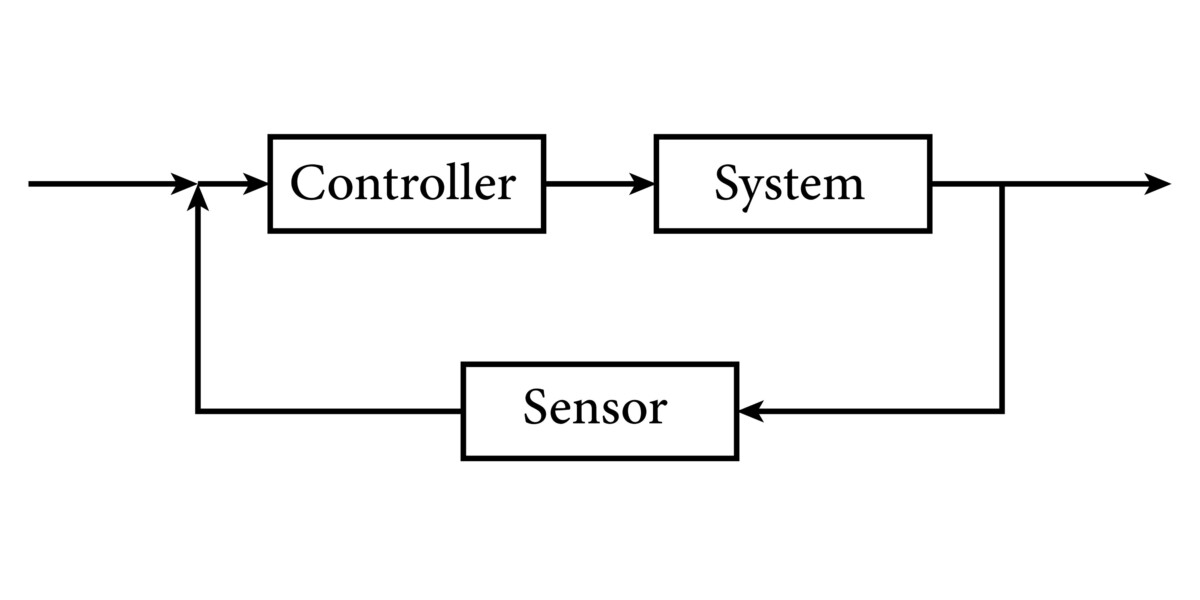
Advanced laboratory systems enable the precise analysis of the transfer function within various processes. This allows for the implementation and comparison of different control laws under real-time constraints. The general form of the controller output is a fundamental study point for understanding system stability:
Controller Output = (Kp * error) + (Ki * integral of error) + (Kd * derivative of error)
By utilizing high-speed data acquisition, researchers can analyze the impact of the proportional (Kp), integral (Ki), and derivative (Kd) gains on settling time, overshoot, and steady-state error. This empirical interaction provides a profound understanding of system stability that software-only models cannot replicate.
Chemical Reaction Kinetics
In Chemical Engineering, understanding the kinetics of reactions within a controlled environment is vital for process optimization. Technical teaching platforms in this domain allow for the experimental determination of reaction rates and activation energies. For a first-order reaction, students can validate the relationship:
Reaction Rate (rA) = k * (Concentration of A)^n
Through modular chemical reactors, it is possible to introduce controlled disturbances, enabling the study of the robustness of thermal and concentration control loops. This capability is essential for graduate-level research focused on reactor stability, efficiency, and safety protocols in industrial environments.
Mechatronics and Automation: Multidisciplinary Integration
Modern industrial environments require a synergy of mechanical, electrical, and computer engineering. Laboratory equipment must reflect this multidisciplinary reality to prepare students for the complexities of modern manufacturing.
Modular Architecture and Scalability
Scalability is a critical factor for university departments managing long-term capital expenditure. Modular platforms allow an institution to begin with foundational units in Industrial Automation and expand into full-scale Smart Factory concepts. This modularity ensures that the laboratory remains compatible with evolving research needs and new industrial standards.
Industrial Standard Integration: PLC and SCADA
To ensure research applicability, laboratory systems must incorporate industrial-grade components. Key elements include:
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC): Integration of industrial units (e.g., Siemens, Allen-Bradley) allows mastery of IEC 61131-3 programming.
- SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition): Systems that enable high-speed data logging, remote process monitoring, and historical trend analysis.
- Real-Time Diagnostics: Tools for simulating fault scenarios, essential for studying process safety and reliability.
Research Capability and Advanced Data Analytics
Beyond undergraduate instruction, advanced pedagogical systems are engineered to support doctoral research. The open-control architecture of these units allows researchers to bypass standard interfaces and implement custom algorithms, such as Model Predictive Control (MPC) or Artificial Intelligence-driven diagnostics, directly onto the physical hardware.
System Modeling and Simulation
Modern laboratory units act as the physical counterpart to Digital Twins. By synchronizing hardware with virtual models, departments can conduct advanced research in predictive maintenance and system optimization. This capability is vital for publications in journals focused on automation and control systems.
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
In alignment with global research priorities, these platforms allow for the quantitative analysis of energy consumption within industrial loops. Researchers can evaluate the efficiency of heat exchangers or the power factor of motor drives, contributing to the development of more sustainable manufacturing methodologies.
Accreditation and Learning Outcomes
For engineering faculties, laboratory acquisition is inextricably linked to accreditation frameworks like ABET. These bodies require measurable evidence that students have developed specific practical competencies.
Pedagogical systems designed with academic rigor support these outcomes by:
- Experimental Proficiency: Demonstrating the ability to design and conduct experiments, as well as to analyze and interpret complex data sets.
- Engineering Tool Usage: Ensuring familiarity with the standard tools and software platforms used in global industry.
- Real-World Problem Solving: Exposure to industrial-grade disturbances and fault scenarios that prepare students for professional challenges.
Industry 4.0 and the Smart Laboratory
The final frontier in engineering education is the integration of Industry 4.0 concepts, including the Internet of Things (IoT) and Cyber-Physical Systems. EDIBON has addressed this by developing “Smart Factory” environments where decentralized control and vertical system integration can be studied empirically.
These laboratories provide a space where students from different departments — Mechanical, Electronics, and Software Engineering — can collaborate on a single, complex industrial sequence. This cross-departmental collaboration is the hallmark of the world’s leading engineering programs.
The selection of laboratory equipment for a high-level engineering faculty is a decision that defines the institution’s research and pedagogical trajectory. Systems that offer a combination of modularity, industrial-grade components, and academic rigor provide the necessary infrastructure to bridge the gap between theory and application.
By integrating mechatronics automation with advanced units in Process Control and Chemical Engineering, universities can ensure their laboratories are not only teaching spaces but also hubs for technological innovation. In an era of rapid industrial disruption, providing students and researchers with scalable, high-fidelity platforms is the ultimate differentiator for academic excellence.




